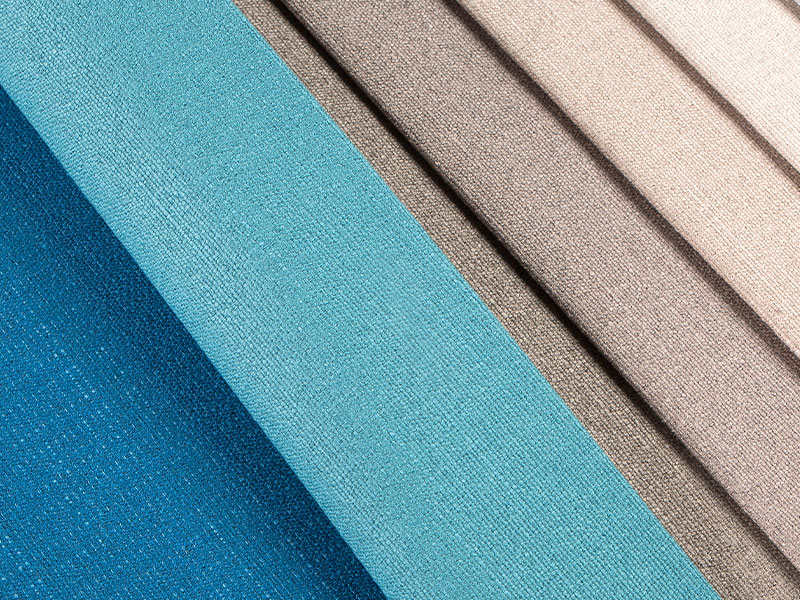
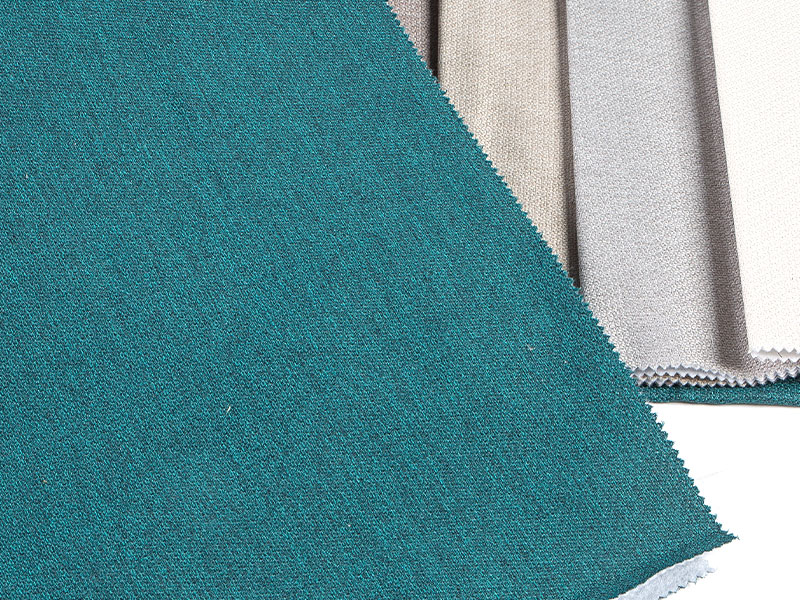
What materials are commonly used in the production of imitation linen fabric?
Imitation linen fabric is designed to mimic the appearance and texture of natural linen while often incorporating synthetic or blended materials. Commonly used materials in the production of imitation linen fabric include:
Polyester:Polyester is a popular choice in imitation linen fabric due to its durability, wrinkle resistance, and ease of care. It can be blended with other fibers to enhance the fabric's performance.
Rayon (Viscose):Rayon, or viscose, is another common material used in imitation linen. It has a smooth and silky feel, resembling the natural drape of linen, and can be blended with other fibers to achieve specific properties.
Nylon:Nylon is known for its strength and abrasion resistance. It may be used in imitation linen blends to enhance the fabric's durability, especially in applications where increased strength is desirable.
Cotton:While natural cotton is not synthetic, it is sometimes blended with synthetic fibers to create a more breathable and comfortable imitation linen fabric. The blend can offer the appearance of linen with the softness of cotton.
Acrylic:Acrylic fibers can be used to add bulk and softness to imitation linen fabric. Blending acrylic with other fibers can contribute to a more luxurious and comfortable feel.
Polypropylene:Polypropylene is a synthetic fiber that is lightweight and resistant to moisture. It may be incorporated into imitation linen for its moisture-wicking properties and quick-drying characteristics.
Microfiber:Microfiber, often made from polyester or a blend of polyester and polyamide, is known for its softness and fine texture. It may be used to create imitation linen with a smooth and silky feel.
Blended Fabrics:Many imitation linen fabrics are created through blending different fibers to achieve a combination of desired characteristics. For example, a polyester-rayon blend might offer a balance between durability and softness.
Additionally, advancements in textile technology may introduce new synthetic fibers or blends for creating high-quality imitation linen fabrics.
Can you explain the manufacturing process of imitation linen fabric and how it differs from genuine linen?
The manufacturing process of
imitation linen fabric involves the use of synthetic or blended fibers to replicate the appearance and texture of natural linen. Here is a general overview of the manufacturing process for imitation linen and how it differs from genuine linen:
1. Fiber Selection:
Imitation Linen:Synthetic fibers such as polyester, rayon, nylon, acrylic, and other blends are commonly used. The choice of fibers depends on the desired characteristics of the final fabric.
Genuine Linen:Derived from the flax plant, linen is a natural fiber known for its strength, breathability, and natural texture.
2. Spinning:
Imitation Linen:Synthetic fibers are often extruded or spun into yarns using modern spinning techniques. The process allows for precise control over the thickness and characteristics of the yarn.
Genuine Linen:The flax fibers from the plant are typically combed and then spun into yarn. The spinning process for linen is generally coarser than that of synthetic fibers.
3. Weaving:
Imitation Linen:Yarns are woven into fabric using various weaving techniques. The choice of weave pattern contributes to the appearance and texture of the fabric.
Genuine Linen:Linen fabrics are woven using traditional looms. The weave pattern can vary, and linen is known for its natural slubs and irregularities, contributing to its distinctive texture.
4. Dyeing and Finishing:
Imitation Linen:Synthetic fibers can be easily dyed using a variety of methods. The finishing process may include treatments to enhance softness, reduce wrinkles, or add other desirable characteristics.
Genuine Linen:Linen fabrics are dyed using natural or synthetic dyes. Linen may have a slightly different color appearance compared to imitation linen due to its natural fibers.
5. Texture and Appearance:
Imitation Linen:Manufacturers use various techniques to create the appearance of linen, such as special weaves, finishes, and printing patterns that mimic the natural texture of linen.
Genuine Linen:The natural irregularities in the fiber and the weaving process contribute to the unique texture of linen. Linen often has a slightly coarse and textured feel.
6. Properties and Characteristics:
Imitation Linen:The final fabric aims to replicate the look and feel of linen while often offering additional benefits such as enhanced durability, wrinkle resistance, and color retention.
Genuine Linen:Linen is prized for its natural breathability, moisture-wicking properties, and a unique texture that becomes softer over time.
7. Environmental Impact:
Imitation Linen:The production of synthetic fibers can have environmental implications. However, advances in sustainable practices may lead to eco-friendly options.
Genuine Linen:Linen is considered a more sustainable option due to its biodegradability and the minimal use of pesticides and water in flax cultivation.
While imitation linen aims to capture the aesthetic qualities of genuine linen, it may lack some of the natural characteristics and sustainability aspects associated with the authentic fiber. Advances in technology and sustainability practices continue to influence the manufacturing processes of both imitation linen and genuine linen fabrics.



 Language
Language  English
English 中文简体
中文简体 عربى
عربى